IUD vs. Implant: What Is the Difference?

These days, contemporary medicine includes more than ten different methods of birth control. Namely, a person might choose between a wide range of condoms, cervical caps, contraceptive pills, vaginal gels, intrauterine devices, birth control implants, and other ways to protect oneself from unwanted pregnancy.
While both intrauterine devices (IUDs) and birth control implants (BCIs) belong to the most innovative, efficient, and long-lasting birth control methods, it might be difficult to define which one will fit your needs best. Thus, how about taking a closer look at both of them to figure out how far they differ?
Before we start: It is a task of an experienced medical professional to define what method of contraception will fit a patient’s needs best.
IUD and BCI as the Most Effective Birth Control Methods
Above anything else, it is high time to check out a short overview of an intrauterine device and birth control implant. Namely, let us go through their definitions, types, and other peculiarities.
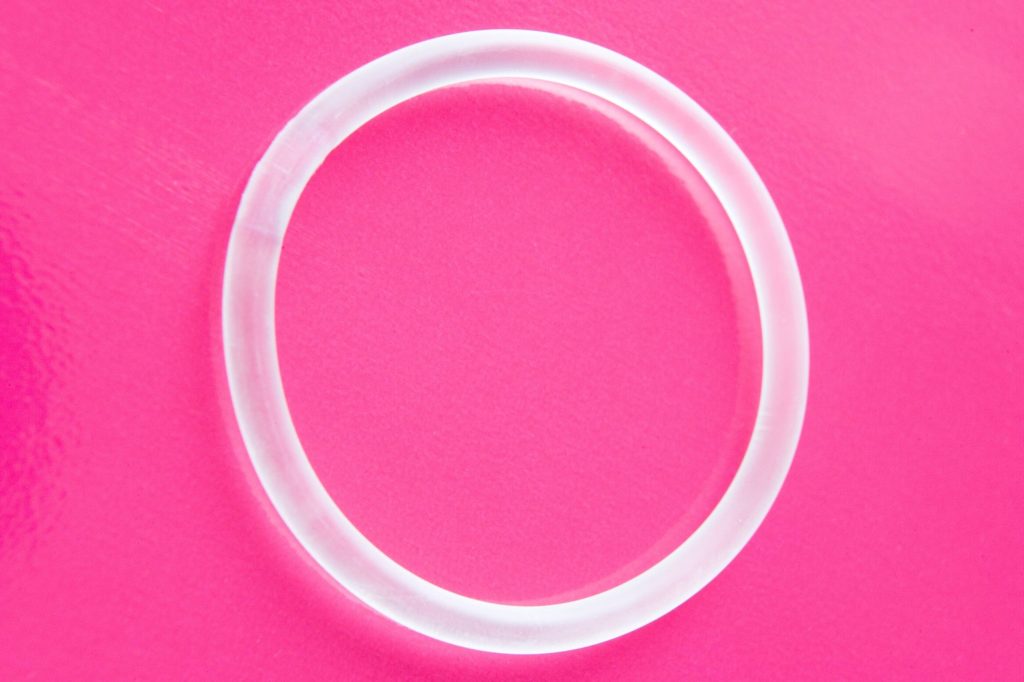
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
An intrauterine device (or, as it is often abbreviated, IUD) is an efficient method to prevent pregnancy for a durable time period. While being one of the most popular birth control choices these days, an IUD is a tiny T-shaped piece of plastic that should be inserted into a patient’s uterus.
Depending on their basic characteristics, all IUDs might be divided into:
- Hormonal IUDs;
- Non-hormonal IUDs.
A hormonal IUD releases synthetically produced hormone progestin, while a non-hormonal IUD is based on copper (and is, therefore, oftentimes referred to as a copper IUD). Below, you will find the list of the most popular brands of hormonal and non-hormonal IUDs:
- Mirena, Kyleena, Liletta, Skyla (hormonal IUDs);
- Paragard (copper IUDs).
Please note: Mirena belongs to the most extensively used IUDs of hormonal nature. It is widely used by patients all over the world. While Paragard, in its turn, is the most popular brand of IUDs of non-hormonal nature. It is a number-one choice for patients who either do not want to or cannot use hormonal methods of contraception.
The insertion of an IUD is a minimally-invasive procedure. However, it should be performed exclusively by a trusted provider of reproductive health care. Under normal circumstances, a patient will get an IUD inserted via the following procedure:
- Above anything else, a medical professional investigates a current health condition of a patient in order to make sure that there exist no contraindications to the insertion of an IUD;
- After making sure that a patient does not have any limitations to the usage of an IUD, a doctor inserts it into the uterus (if needed, a local anesthetic might be applied to reduce discomfort during the procedure).
On average, the whole process of an IUD insertion by a doctor or nurse (together with the cut-off of IUD strings) lasts about only 30 minutes. As soon as the procedure is over, the device starts working. Namely, it prevents pregnancy in the following way:
- On the one hand, an IUD thickens the cervical mucus in order to prevent the sperm from reaching the egg and, therefore, fertilizing it;
- On the other hand, an IUD thins the lining of the uterus in order to prevent the fertilized egg from getting implanted successfully.
All IUDs (no matter whether we are talking about a hormonal or copper IUD) belong to long-acting reversible contraception methods. They provide a patient with the protection of unplanned pregnancy for a time period of up to 10 years. However, if a patient wants to get an IUD removed earlier, it will not continue to protect a patient from becoming pregnant.
Please note: Apart from being an effective birth control method, an IUD might also be used as emergency contraception. Namely, it is likely to protect a patient from unplanned pregnancy in case of being installed within 5 days after the unprotected sex.
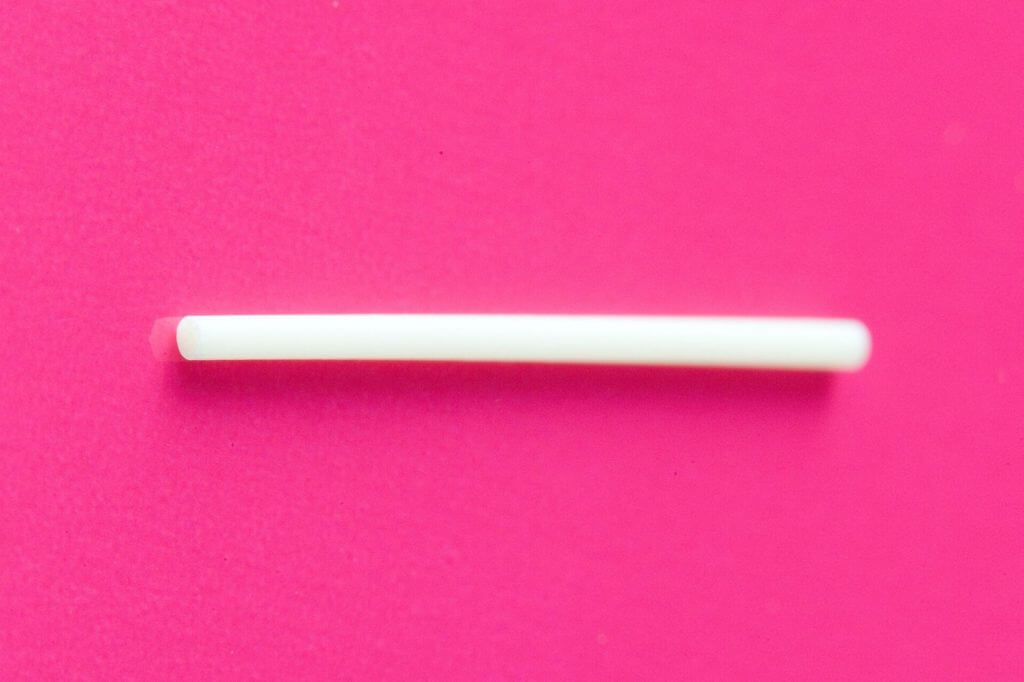
Birth Control Implant (BCI)
A birth control implant (or BCI) is another effective method to protect reproductive rights of a patient for a substantial period of time. It is a thin rod that has the size of a matchstick that should be inserted into an arm of a patient.
A vast majority of birth control implants are hormonal. In other words, they release the hormone progestin into a patient’s body and, therefore, protect them from getting pregnant. Probably the most widely spread brand of birth control implants is Nexplanon.
The working principle of a birth control implant is similar to the one of an IUD. Here is how it looks:
- Beyond everything, a patient has to book an appointment with a medical practitioner who investigates a patient’s current health condition;
- If a patient does not have any contraindications to the insertion of a BCI, a medical practitioner might insert it under the skin of their upper arm.
Shortly after a birth control implant is installed, it starts to protect a patient from unplanned pregnancy by means of releasing progestin, which eventually leads to both the thickening of the cervical mucus and the prevention of the fertilized egg from getting implanted.
The minimally invasive procedure of a BCI insertion has the power to provide a patient with long-lasting contraception that equals 5 years. Due to the fact that this result is not permanent, a patient will be able to get pregnant as soon as it is removed.
Please note: Unlike an IUD, BCI is not usually used as a method of emergency contraception.
Comparison Between an IUD and an Implant
After having a short overview of an IUD and birth control implant, it’s high time to compare and contrast them. So, feel free to review the similarities and differences between these birth control choices.
Similarities
IUDs and BCIs belong to the most popular birth control methods worldwide. By taking their advantages and disadvantages into account, they share the following characteristics:
- Exceptionally high efficiency. Both IUD and BCI provide a patient with more than 99 percent of effectiveness. In other words, less than 1 patient out of 100 will get pregnant while using an IUD or a BCI;
- Reversibility. Neither IUD nor BCI ensures a patient with a permanent result. Therefore, a patient will be able to get pregnant shortly after removing any of these devices;
- Safety. Just like an IUD, BCI is a safe method of contraception. It rarely causes any serious complications. However, a patient might experience temporary side effects after the insertion of the device;
- Limitations. The insertion of an IUD has similar to BCI contraindications. They both should not be used if a patient suffers from a serious health problem (for instance, cancer, AIDS, or liver tumor), experiences vaginal bleeding, or is pregnant;
- Reduction of menstrual symptoms. Similar to IUD, BCI not only protects a patient from unplanned pregnancy but also oftentimes reduces the intensity of such menstrual symptoms as bleeding or painful feelings;
- No protection against sexually transmitted infections. The usage of an IUD, as well as BCI, has little impact on a patient’s sexual health. In other words, it does not protect them against sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea, herpes, or syphilis.
Moreover, both IUDs and BCIs should be inserted by certified medical professionals. Despite the minimal invasiveness of the procedure, it cannot be performed by patients themselves.
Please note: After deciding to insert an IUD or BCI, make sure to find a reliable medical professional. Only this way will you be able to ensure that the procedure is performed correctly and your information is kept confidential (since qualitative planned parenthood respects the safety and privacy of a patient).
Differences
Despite all the above-mentioned similarities between the usage of an IUD and BCI, they have a wide range of differences. Below, you will find the list of the main distinct points between them:
- While there exist both hormonal and non-hormonal (copper) IUDs, all BCIs are hormonal;
- IUDs last longer than BCIs (namely, they might protect a patient for up to 10 years instead of 5 years);
- The place of the insertion of an IUD and BCI is also different (while the first birth control type should be implanted into the uterus, the second one has to be installed into the upper hand of a patient).
Furthermore, the amount of money a patient will have to donate to planned parenthood also depends on whether they choose an IUD or a BCI. Namely, an IUD tends to be slightly more expensive than a BCI.
Please note: A patient has to get ready to spend around 1.500$ for the installation of an IUD and 1.200$ for the installation of a BCI. Luckily, the insertion of both an IUD and BCI might be covered by health insurance in some cases.
Final Words
All in all, both an IUD and BCI belong to the most effective and long-lasting methods of birth control these days. They help millions of patients all over the world to protect themselves from unwanted pregnancies.
Despite sharing a great number of similarities, these methods of birth control have several differences. Thus, it is only up to you and your healthcare professional to decide which one will fit your needs best.
So, make your choice and enjoy any of these durable, convenient, and effective birth control options! Stay healthy at all times.